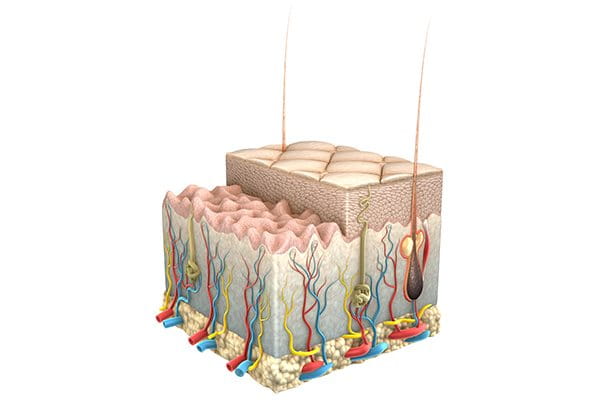
Sensitive skin is skin that is easily irritated and more likely to react to internal and external aggressors than ‘normal’ skin.
Sensitive skin takes many forms: it can be under-developed (in the case of children), inflamed (due to a skin condition such as Atopic Dermatitis , Rosacea or acne) , damaged (as a result of medication or dermatological treatments or simply be the result of someone’s genetics (for example, pale skin tends to be more sensitive to sunlight than darker skins).
You can read more about the causes and symptoms of sensitive skin in Understanding the language of sensitive skin.
Sun in moderation is good for us but overexposure to the sun’s rays can cause both short- and long-term damage. Sensitive skin is particularly prone to sun damage because it has a weaker structure and is less resilient to external aggressors such as the sun.
You can read more about the positive and negative effects of sun on skin in How do UVA, UVB and HEVIS light rays affect skin?
Age has an impact on skin sensitivity: younger and older people are more susceptible to damage from the sun. Paler skin has less melanin than darker skins and so less of skin’s natural protection against the sun’s rays, but darker skins tend to be more prone to hyperpigmentation.
Skin on certain parts of our body – especially the face – is exposed to the environment all year round making it particularly susceptible to the sun. Certain medications, inappropriate skin care and skin conditions such as Atopic Dermatitis all compromise skin’s natural protective barrier making it more susceptible to damage at a cellular level.
All skin needs protecting from the sun, but superior sun protection is particularly important for the following sensitive skin types:
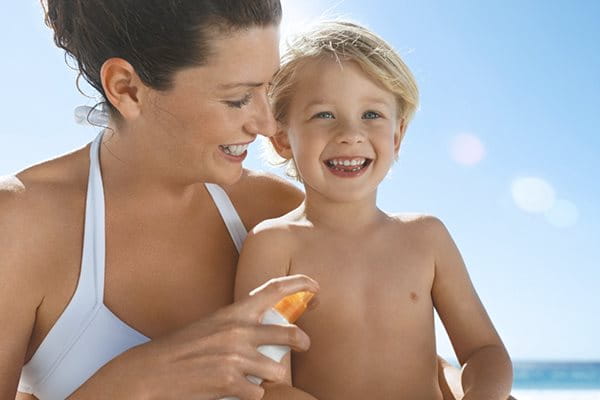

Babies and children have thinner skin than adults which makes it weaker. Many of skin’s natural protective systems such as melanin are also still developing and so their skin is less able to protect itself from the sun’s rays. It’s important to remember that skin damage occurs even before sunburn is visible and that sun-induced skin damage incurred during childhood puts someone at a much higher risk of further skin damage in later life.
You can read more in why do babies and children need special sun protection?
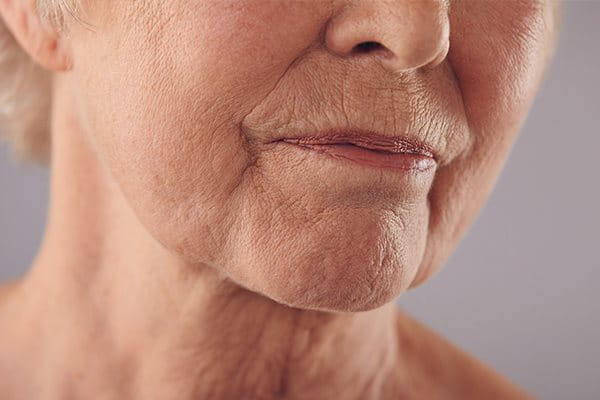
As our skin ages it dries out and becomes thinner. Its protective barrier weakens and it benefits from extra high protection from the sun, even on cloudy days.
You can find out more about how to care for skin as it ages in How does skin age and how should I care for it?
Pale Skin
Pale skin contains less melanin than darker skin types and so is more susceptible to sun damage, but darker skins tend to be more prone to hyperpigmentation.
Facial skin is thinner than skin across most of our body, making it more sensitive to the environment. It’s also less likely to be protected by clothes and so is exposed to the sun’s rays all year round. It benefits from daily protection, even on cloudy days, which is why the Eucerin sun protection range includes products that can be easily incorporated into your daily skincare routine – whatever your skin type or condition. Read more in Why do I need daily sun protection for my face?
Some skin is particularly prone to sun allergies, the most common of which is Polymorphous Light Eruption (or PLE). You can find out about what causes sun allergies, how to help prevent a reaction and how to protect skin prone to sun allergies in Why does skin prone to sun allergies need special sun protection?
Some people with Atopic Dermatitis find that a bit of sun can help, but atopic skin is a dry skin condition and too much sun causes skin to dry out further. You can read more about the causes and triggers of atopic skin as well as how to give it the daily care it needs in Understanding Atopic Dermatitis , How to care for young atopic skin and How to care for adult atopic skin.
The Eucerin Sun range includes sun protection products that are clinically and dermatologically proven to be suitable for atopic skin, giving it the soothing protection that it needs.
Excessive exposure to the sun, and inappropriate sun protection, can exacerbate rather than heal blemishes and acne. Skin which is undergoing medical treatment for acne is particularly sensitive to sunlight and needs very high protection from the sun. You can find out more in Why does oily and acne-prone skin need special sun protection?
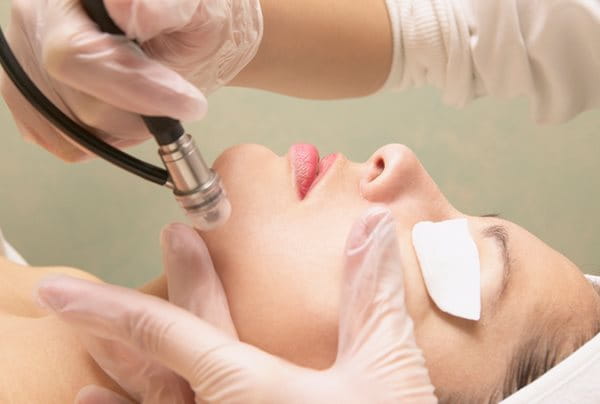
Chemical peels (the products you use at home and the more intense treatments used by dermatologists) resurface skin and make it more sensitive to sunlight and potential sun damage. You can find out more in Chemical peels: How do they work and how should I care for skin afer treatment?
Both ablative and non-ablative laser therapy also sensitize skin and makes is more susceptible to sun damage. Find out more in Laser therapy: How should I care for my skin afer treatment?Dermatologists recommend that you avoid direct sunlight following a treatment and that you wear the highest possible sun protection even in the shade.
It’s not just acne medication that heightens skin’s sensitivity to the sun. Many commonly-used medications – both topical and systemic (oral) – can cause photosensitivity.
Issues of photosensitivity are most commonly associated with the following medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers (e.g. Ibuprofen)
- Antibiotics
- Anticonvulsants (antiepileptic drugs)
- Antifungals
- Diuretics
- Retinoids
- Statins
The best way to protect skin is to limit the time spent in the sun, avoid it during its most intense hours, wear protective clothing and apply a superior sun protection product that offers the level of protection that your skin needs. Ideally, in addition to UV protection, the product you use should also offer high-energy visible (HEVIS) light defense. We also recommend that you use sun protection products that have been specially formulated for your skin type and condition.
You can read more about how to minimize the risks of exposure, how to choose the right sun protection products for your skin and how best to apply them in Why do I need daily sun protection for my face? and How should I protect my body from the sun?
Eucerin’s innovative Advanced Spectral Technology combines broadband and photostable UVA/UVB filters1 for superior UV protection with antioxidant Licochalcone A for HEVIS light defense. Many products in the range also include Glycyrrhetinic Acid which provides additional DNA protection.
The Eucerin sun protection range includes products that have been specially formulated to skin different skin types and conditions with a range of textures and active ingredients proven to address particular skin concerns.
- Meeting the highest standards for UVA and UVB protection as defined by Cosmetics Europe. The levels of UVA protection are higher than the EU requirement








